The Annual Information Statement (AIS) is a comprehensive document introduced by the Income Tax Department of India to improve transparency and promote voluntary tax compliance. It provides taxpayers with a detailed summary of their financial transactions across various sources for a financial year, enabling them to cross-verify their income and tax-related data before filing Income Tax Returns (ITR).
In this article, we’ll explain what AIS is, how to check your AIS status online, how to open the AIS PDF file, and how to give feedback on any incorrect entries.
What is Annual Information Statement (AIS)?
The Annual Information Statement (AIS) is a consolidated record of a taxpayer’s financial transactions for a financial year. It includes details like income, tax deductions, interest earned, share transactions, mutual fund investments, TDS/TCS, and other high-value transactions. AIS is an extended version of the earlier Form 26AS and is available through the Income Tax Department’s e-filing portal.
The purpose of AIS is to enhance taxpayer awareness and facilitate voluntary compliance by offering a ready-made summary of income-related activities reported by various entities.
How to Check Annual Information Statement (AIS)
The Annual Information Statement (AIS) provides a detailed summary of your financial transactions as reported to the Income Tax Department. It includes data like income, TDS, interest, dividend, securities, and other specified financial transactions.
Follow these steps to access your AIS through the official Income Tax e-Filing portal:
Step 1: Visit the Income Tax Portal
Go to the official website of Income Tax Department
Click on the “Login” button at the top right corner of the homepage.
Once logged in, navigate to the top menu and select: AIS (Annual Information Statement)
Step 2: Click on the ‘Proceed’ button.
Step 3: You’ll be redirected to the AIS compliance portal. On the homepage, you’ll find both the Taxpayer Information Summary (TIS) and the Annual Information Statement (AIS) displayed alongside helpful instructions for navigating the portal.
Step 4: Choose the financial year, then click on either the AIS or TIS tile to see the details.
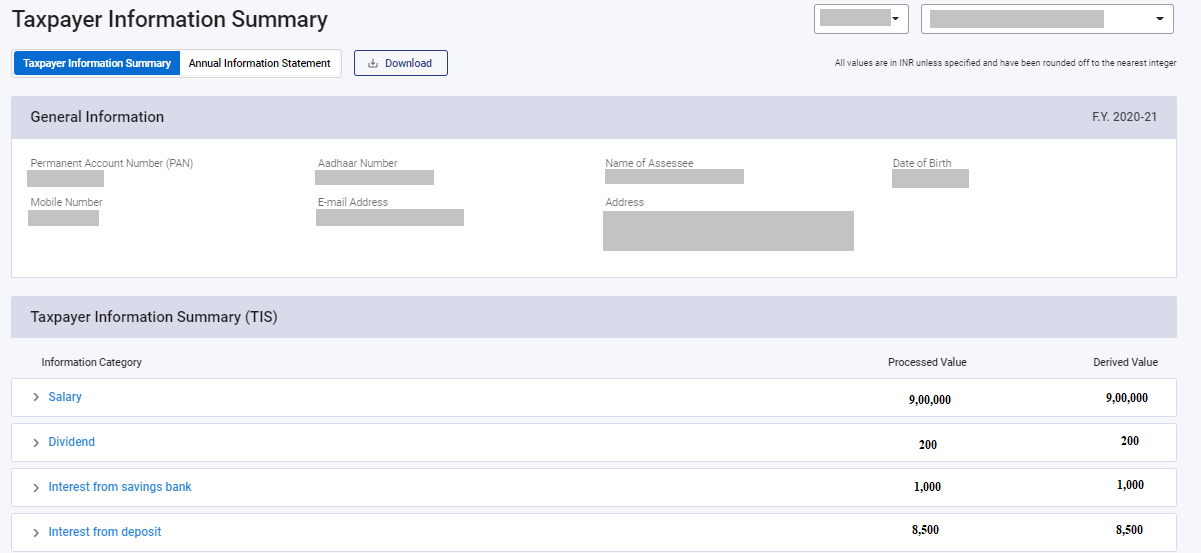
You can view the summary of AIS
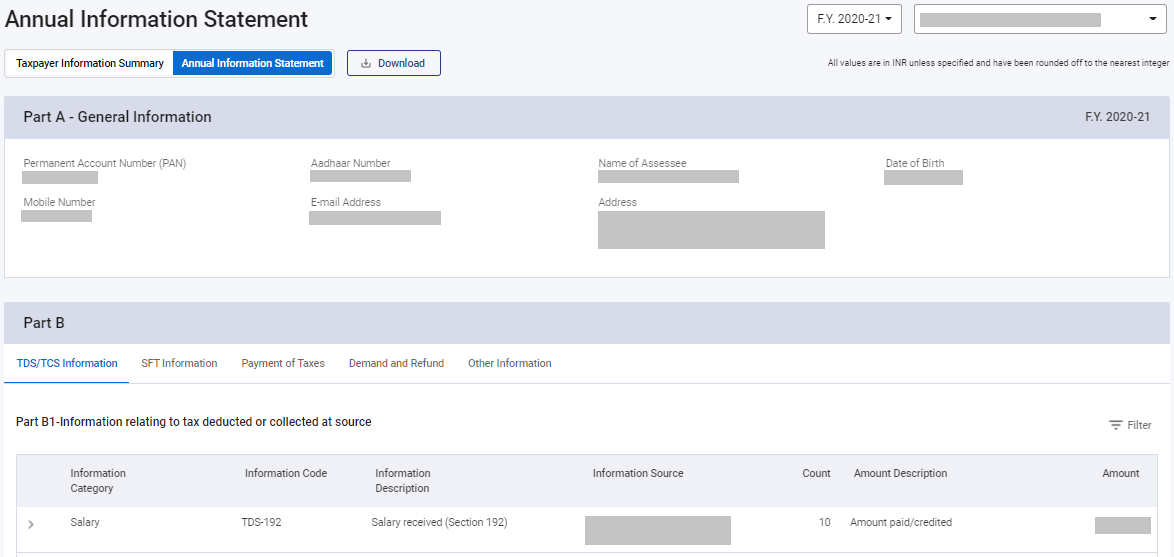
Key Features of AIS
Comprehensive Coverage: AIS includes salary, interest, dividends, rent, mutual fund redemptions, share trades, foreign remittances, and more.
Two-Part Structure: AIS consists of Part A and Part B.
Part A covers basic taxpayer information and TDS/TCS details.
Part B includes Statement of Financial Transactions (SFT), tax payments, demand/refund, and other specified information.
Dynamic Feedback System: Taxpayers can respond to discrepancies or mismatches by submitting feedback directly through the portal.
Downloadable Formats: AIS can be downloaded in PDF, JSON, and CSV formats.
Updated Information: If corrected data is submitted by reporting entities, the AIS is updated accordingly.
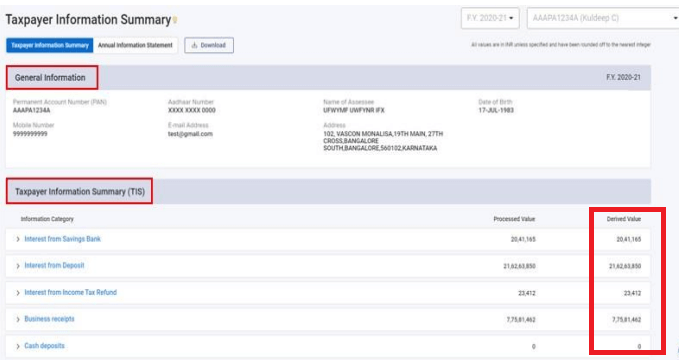
Access to Taxpayer Information Summary (TIS): A simplified version of AIS, summarizing income heads and showing pre-filled values used in ITR.
Difference Between AIS and Form 26AS
| Criteria |
AIS |
Form 26AS |
| Scope |
Extensive: Includes SFTs, TDS, interest, etc. |
Limited: Mostly TDS/TCS and refunds |
| Format |
Available in PDF, JSON, CSV |
Available in PDF format only |
| Format |
Available in PDF, JSON, CSV |
Available in PDF format only |
| Information Sources |
Banks, stock exchanges, mutual funds, etc. |
Mainly employers and deductors |
| Feedback Option |
Yes |
No |
| Summary for ITR Filing |
Yes (via TIS) |
No |
Who Can Access AIS?
Any registered taxpayer on the Income Tax e-filing portal can access their AIS. It is available for individuals, HUFs, and businesses with a valid PAN.
How to Submit Feedback on AIS?
Submitting feedback in your AIS (Annual Information Statement) is an important step if you find any discrepancy or incorrect information in your tax data. The Income Tax Department allows taxpayers to provide feedback directly through the AIS portal, helping ensure your ITR reflects accurate information and avoids mismatch notices.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to submit feedback in AIS:
Go to AIS Section: Log in to the Income Tax portal and open the AIS tab from the compliance portal.
Choose the Entry: Select the specific category (like SFT or TDS) and find the entry you want to correct.
Submit Feedback: Click “Provide Feedback,” choose the right option, add your remarks, and submit.
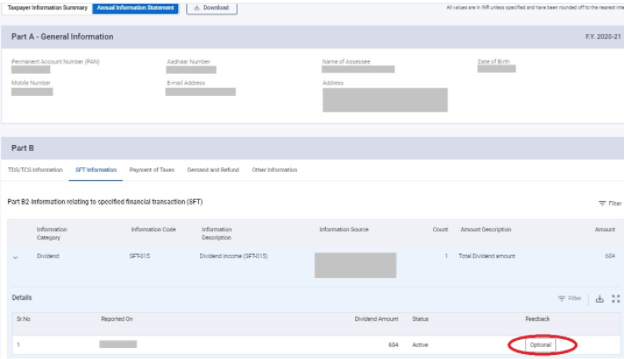
Step 4: Select the relevant feedback category as shown on the screen.
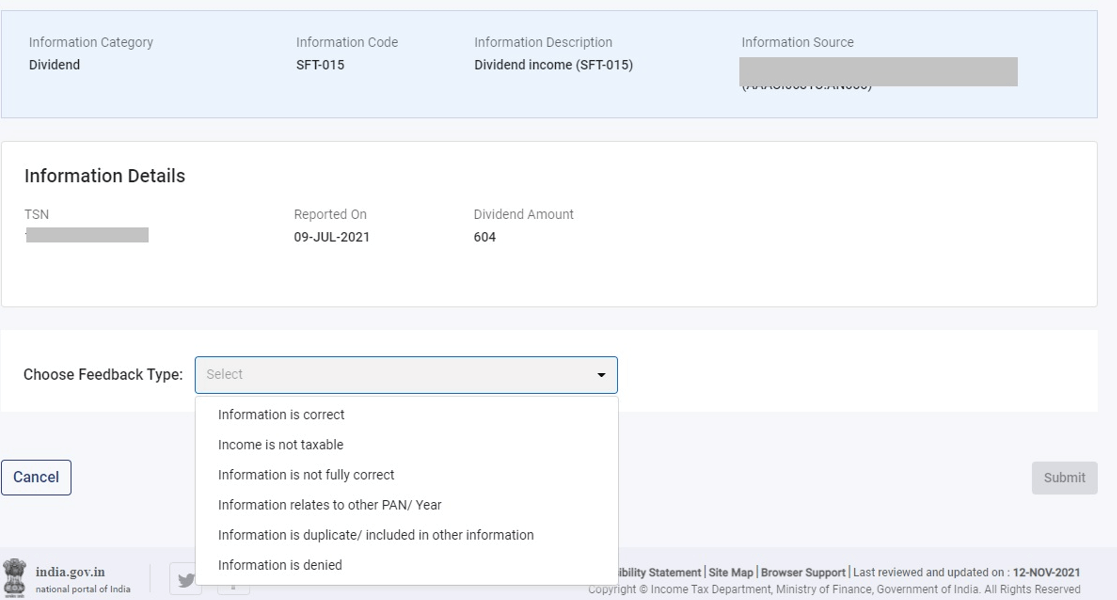
Step 5: Once submitted, the updated value will be displayed within the brackets
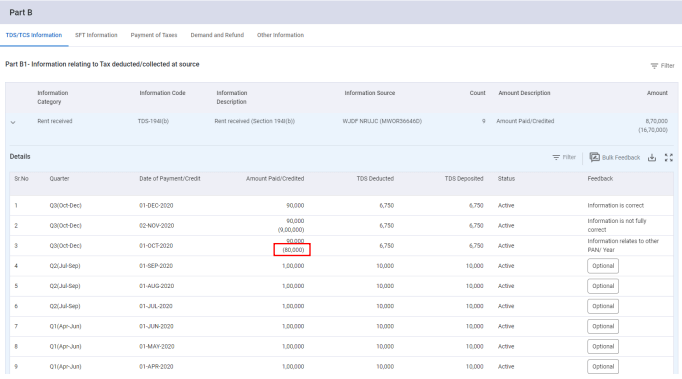
Step 6: The updated amount also reflects in the Taxpayer Information Summary (TIS), which is later utilized to prefill the ITR form for the taxpayer.
What to Do If You Find an Error in AIS or Form 26AS?
The Annual Information Statement (AIS) and Form 26AS are based on data collected from various financial institutions, employers, and reporting entities. These entities are legally required to report certain financial transactions - especially high-value ones - to the Income Tax Department. Once this data is received, it’s displayed in your AIS. However, sometimes this information may be missing, duplicated, or reported inaccurately.
Since AIS relies on third-party reporting, it’s possible that certain entries may not reflect the actual transactions accurately or may be delayed in getting updated. For example, interest income from banks, stock transactions, or TDS entries may be incomplete or wrongly reported.
As a taxpayer, it’s your responsibility to carefully verify every detail shown in AIS and ensure that your ITR reflects the correct figures. Ignoring discrepancies can lead to notices, demands, or penalties, especially in cases where your declared income in ITR does not match what’s reported in AIS.
Recently, the Income Tax Department flagged thousands of cases where the data in AIS did not match the filed ITRs. In such situations, the mismatch is treated as underreporting of income, unless corrected in time. To avoid complications like reassessment, interest, or penalty, it’s essential to act quickly and responsibly.
Importance of Reviewing AIS Before Filing ITR
Before filing your ITR, it is strongly recommended to review your AIS. This helps ensure:
- You report all incomes accurately
- There is no mismatch that could lead to a notice
- You avoid interest, penalties, or reassessment
Mismatches in income, interest, dividends, or capital gains can lead to scrutiny under Sections like 143(1) or 139(9).
Key Takeaways
- AIS is a consolidated statement of your financial transactions with the Income Tax Department.
- It includes all reported incomes, TDS, interest, mutual fund transactions, foreign remittance, etc.
- Taxpayers should always review AIS before filing ITR to avoid errors.
- If any data is wrong, you can submit feedback directly through the portal.








